Make a Python Servo Program Run Again
Contributors: El Duderino
Decision-making a Servo with Python and Pi Servo pHAT
Our tertiary example demonstrates how to drive a servo using a Raspberry Pi and the SparkFun Servo pHAT for Raspberry Pi with the SparkFun PiServoHAT Python Module. The Servo pHAT tin can control upward to xvi PWM devices and then it is a great choice for projects using multiple servos forth with other PWM devices like LEDs. The Raspberry Pi also has much more than processing power than a evolution board like the RedBoard we used in the previous example so you can run all sorts of processes in the background for a complex project.
If you take never used a Raspberry Pi or the Servo pHAT before, we highly recommend reading through these tutorials before proceeding. The Getting Started with the Raspberry Pi tutorial is the most important in order to fix your Raspberry Pi as you cannot keep with this case without starting time configuring your Pi.
Required Materials
To follow along with this instance, y'all will need the following materials. Depending on what parts y'all already have, or if you would like to use a different Raspberry Pi or servo, y'all can arrange your cart appropriately.
Along with these parts, you will want a keyboard, mouse and monitor to connect to your Raspberry Pi to configure and interact with it. Alternatively, y'all can utilize another computer to do a headless setup for your Raspberry Pi. Too, if you already have a suitable SD card you would like to utilise, you can download and install the Raspbian OS for the Pi from the Raspberry Pi Foundation following the instructions from their Setting up your Raspberry Pi guide.
Hardware Hookup
Hooking everything up with the Servo pHAT is pretty straightforward merely there are a few things to annotation. With everything powered off, plug the pHAT on to the Pi'due south 2x20 GPIO Header, taking care to marshal it properly so it looks like the photos below.
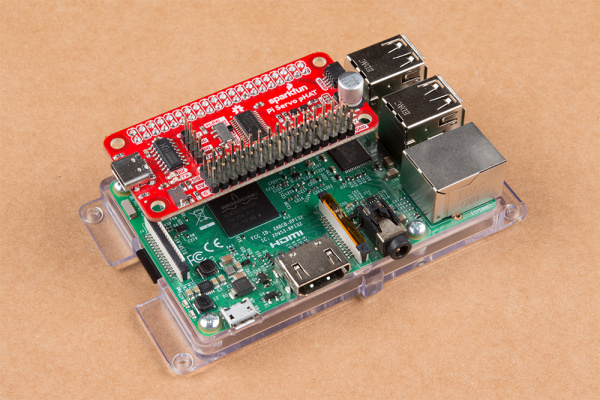

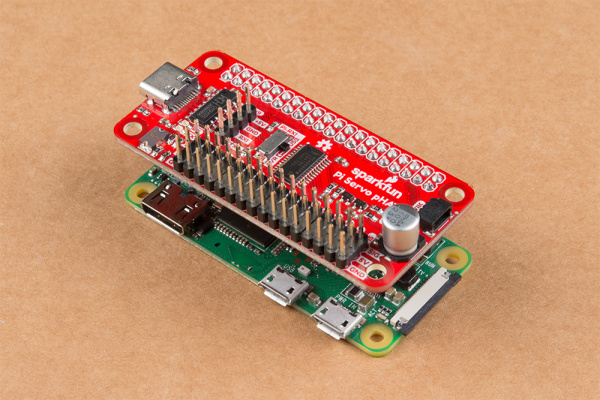
Pi Servo pHAT properly connected to a Raspberry Pi three (left) and Raspberry Pi Zilch W (correct). Click prototype to overstate.
Side by side, connect your servo to one of the 3-pivot aqueduct headers taking care to match the pins on the servo with the silkscreen labels on the Servo pHAT. The example we are using defaults to Channel 0 so, if you lot use a different channel, brand sure to suit the lawmaking accordingly. Do not connect servos to the Pi while it is powered on as the resulting electric current spike can crusade the Raspberry Pi to reset.
At present, go ahead and plug in your Pi. And then plough it on and we're gear up to motility on to programming. The photos below show two options for powering the Raspberry Pi and Pi Servo pHAT.
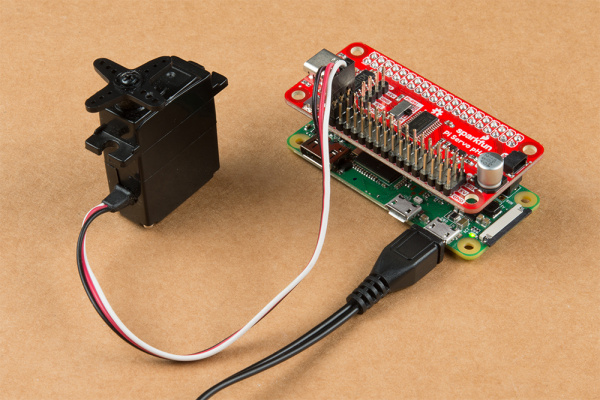
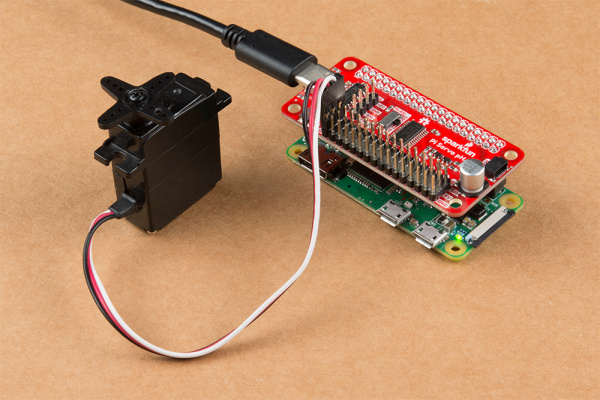
Examples of 2 of the various power supply options.
Python Bundle
With all of the hardware assembled and your Pi configured and gear up to become, information technology is time to install the Python module and run 1 of the examples. For this particular experiment, we'll use Example ii - Full Sweep with 180 deg. Servo.
First, we need to install the package to our Pi. For the sake of keeping this tutorial short we'll but cover how to install the entire SparkFun Qwiic Python package. If you would like to install individual parts of the parcel or install them manually, please head on over to this section of our Hookup Guide for the Servo pHAT for detailed instructions.
The SparkFun Qwiic Python Bundle installs all the bachelor Python packages for our Qwiic products and includes the required I2C driver bundle. On systems that back up PyPi via pip3 (utilise pip for Python ii), installation is elementary using the post-obit commands:
For all users (note the user must take sudo privileges) enter the following command from your command prompt:
language:bash sudo pip3 install sparkfun-qwiic If you just want to install the package for the electric current user enter this command in your command prompt:
linguistic communication:bash pip install sparkfun-qwiic With the SparkFun Qwiic bundle installed it is time to create and run our code. Yous can either download or copy the code below into a file. Then open up/save the file and execute the code in your preferred Python IDE. For example, to run the case in the default development environment on Raspbian, IDLE, click Run>Run Module or use the F5 fundamental. To stop the instance, apply the Ctrl + C key combination.
While the example is running, you lot should see your servo moving back and forth over a 180 degree arc.
language:python #----------------------------------------------------------------------- # Pi Servo Hat - Case 2 #----------------------------------------------------------------------- # # Written by SparkFun Electronics, June 2019 # Author: Wes Furuya # # Compatibility: # * Original: https://www.sparkfun.com/products/14328 # * v2: https://world wide web.sparkfun.com/products/15316 # # Do you like this library? Help support SparkFun. Buy a board! # For more information on Pi Servo Hat, check out the product page # linked higher up. # # This program is distributed in the hope that information technology will exist useful, but # WITHOUT Any WARRANTY without fifty-fifty the implied warranty of # MERCHANTABILITY or Fitness FOR A Item PURPOSE. Run into the GNU # General Public License for more than details. # # You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License # along with this program. If non, run across <http:www.gnu.org/licenses/>. # #======================================================================= # Copyright (c) 2019 SparkFun Electronics # # Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining # a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the # "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including # without limitation the rights to use, re-create, modify, merge, publish, # distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to # permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to practise so, subject to # the following weather condition: # # The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be # included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software. # # THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, # Limited OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING But NOT Express TO THE WARRANTIES OF # MERCHANTABILITY, Fitness FOR A Item PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. # IN NO Consequence SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY # Claim, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN Action OF CONTRACT, # TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE # SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE. #======================================================================= """ This example should be used with a 180 caste (range of rotation) servo on channel 0 of the Pi Servo Hat. The extended code (commented out), at the end of the example could exist used to examination the total range of the servo motion. Still, users should be wary as they can damage their servo by giving it a position exterior the standard range of motion. """ import pi_servo_hat import fourth dimension # Initialize Constructor exam = pi_servo_hat.PiServoHat() # Restart Servo Hat (in example Lid is frozen/locked) examination.restart() # Test Run ######################################### # Moves servo position to 0 degrees (1ms), Channel 0 exam.move_servo_position(0, 0, 180) # Interruption one sec time.slumber(1) # Moves servo position to 180 degrees (2ms), Aqueduct 0 examination.move_servo_position(0, 180, 180) # Suspension 1 sec time.sleep(1) # Sweep ######################################### while True: for i in range(0, 180): print(i) examination.move_servo_position(0, i, 180) time.sleep(.001) for i in range(180, 0, -1): impress(i) test.move_servo_position(0, i, 180) time.sleep(.001) ######################################### # Code below may harm servo, use with caution # Test sweep for total range of servo (outside 0 to 180 degrees). # while Truthful: # for i in range(-45, 200): # print(i) # exam.move_servo_position(0, i, 180) # fourth dimension.sleep(.001) # for i in range(200, -45, -i): # print(i) # test.move_servo_position(0, i, 180) # time.slumber(.001) Troubleshooting Tips
If you are having whatsoever difficulty getting your servo to move or recognize the Servo pHAT on your Pi, hither are a few tips to aid troubleshoot.
No Available Devices
If you see this error readout: OSError: [Errno 121] Remote I/O error, double check your connections to the GPIO header.
As well make sure that the I2C hardware is enabled on your Raspberry Pi. If it is non enabled, you will probably see this mistake readout: Failed to connect to I2C bus 1.. If you need assistance enabling I2C on your Pi, take a expect at this section of our Raspberry Pi: SPI and I2C Tutorial.
Check your I2C Connection
A simple method to check if your Raspberry Pi tin can communicate with the Servo pHAT over I2C is to ping the I2C bus. On the latest releases of Raspbian Stretch, the i2ctools package should come pre-installed. If information technology isn't run the following control in the concluding:
linguistic communication:bash sudo apt-become install i2ctools With the i2ctools packet is installed, you tin can ping the I2C coach with the following command in the final:
language:bash i2cdetect -y 1 You should run into a table printed out in the terminal. If the Servo pHAT is connected and working properly you should run across the address space for 0x40 marked with 40.
Electric current Draw Problems
If your servos are drawing more than current that your power supply can handle, your Servo pHAT will not operate correctly and the Raspberry Pi may reboot or chocolate-brown out intermittently.
If you have a specially big servo, or many servos driving a heavy load, you lot might detect the Pi rebooting or browning out when using the USB port on the Pi to power both the Pi and the Servo pHAT. You tin try switching to powering the Pi and Servo pHAT directly through the USB-C connector on the pHAT, just a better solution is to sever the Power Isolation jumper and power each device individually. We cover where to locate that jumper and how to modify information technology in the "Jumpers" subsection of the Hardware Overview section of the Servo pHAT Hookup Guide.
Source: https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/basic-servo-control-for-beginners/controlling-a-servo-with-python-and-pi-servo-phat
0 Response to "Make a Python Servo Program Run Again"
Post a Comment